What are business processes?
Business process definition
A business process is a systematic sequence of activities or tasks performed within a company or organization to achieve a specific business outcome. These activities may involve manual or automated tasks and are organized in a defined order to ensure efficient and effective execution.
Business process requirements according to ISO 9001
The requirements for business processes result from ISO 9001:2015. The standard specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that is implemented within a company. The requirements for business processes relate to the following aspects:
- Business process orientation: The QMS must be geared to business processes and enable systematic and continuous improvement of the processes.
- Business process documentation: Business processes must be documented to enable clear identification and monitoring.
- Business Process Control: Business processes must be controlled to ensure they are continuously improved and run efficiently.
- Business process evaluation: The performance of business processes must be regularly monitored and evaluated in order to identify and correct possible weaknesses.
- Responsibility and competence: Each process participant must be responsible for their role and responsibility in the process and have the necessary competence.
- Business Process Coordination: Business processes must be coordinated in a way that enables smooth interaction and integration with other processes.
The importance of business processes for companies
Companies, especially during the start-up phase, often lack business processes. There is a lack of clear responsibilities, information is stored in different documents and processes change spontaneously. This leads to work being carried out inefficiently and involves high friction losses.
Correct business processes are of enormous importance to companies as they determine the way a company works and does business. They represent the basis for an efficient and successful business activity and have a direct influence on the performance, productivity and profitability of a company.
d.velop process studio
Digitize your business processes
Easily adapt digital business processes to your individual requirements at any time with our visual editor – simply and without any IT knowledge. You also have the option of seamlessly integrating external systems via interfaces.
- No-code approach
- Easy modelling
- Connection of further systems and data
What business processes are there?
There are a variety of business processes in companies and organizations. We have identified some common business processes and their potential for optimization for review:
Contract management process
A well-designed contract management process is essential to effectively managing contracts and meeting all contractual obligations. Such a business process can help minimize risk for companies and increase the chances of economic success.
The contract management process is a set of steps and activities aimed at managing the lifecycle of a contract , from development to monitoring and review. The aim is to ensure smooth and efficient handling of contracts in order to minimize the risk of breaches and financial losses.

Webinar Contract management
Collaborative Contract Lifecycle Management for Microsoft 365
Increase transparency and thus keep track of contracts and deadlines.
And stop losing 9% of your annual turnover due to contract management!
Learn in the webinar what digital contract management with Microsoft 365 looks like and how you can benefit. Look forward to a live demo of the solution. Afterwards you can test-drive the solution and convince yourself.
Procurement process
Procurement processes describe the sequence of activities that are required for the procurement of goods and services. These business processes include identifying needs, selecting suppliers, negotiating prices and terms, monitoring deliveries, and billing costs.
The digitization of procurement contributes to efficient and transparent procurement management, which in turn contributes to the effective use of resources, compliance with the budget, risk minimization and quality assurance of the purchased goods and services.
HR processes
HR processes (Human Resource Processes) are the business processes within human resources management in a company. These processes encompass a variety of activities ranging from recruiting and selecting employees to staff development and mentoring. This includes processes such as payroll accounting and payroll accounting, timekeeping, personnel administration, employee promotion, as well as the management of sickness and holiday requests.
The goal of HR processes is to efficiently and effectively manage the company’s human resources to support the company’s goals and success. Optimal HR management contributes to a good working atmosphere, high employee satisfaction and improved employee loyalty.
Logistics process
Logistics processes are business processes that are responsible for planning, controlling, along with monitoring the flow of materials and information in a company. This involves the efficient and economical management of the flow of goods from procurement through production to distribution to the customer. Logistics processes have a crucial impact on efficiency, flexibility, aligned with achieving customer satisfaction. They enable a company to deliver products to its customers quickly, on time and at a reasonable cost.
An effective logistics process also includes measures to minimize storage costs and overstocks, as well as efficient control of warehousing and movements. A reliable supply chain, monitoring of inventories and delivery times, are also important tasks in logistics management.
IT process
IT processes serve to support, automate and improve the business processes of a company through the use of information technology. Business and IT processes are therefore closely linked, both supporting and complementing each other. In practice, business and IT processes work in close cooperation by defining business requirements, selecting and implementing IT systems, integrating data and evolving IT solutions. A high-quality IT infrastructure can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of IT processes. It is, therefore, critical IT processes and IT infrastructure are coordinated and developed in close cooperation.
Sales process
A sales process, like the order-to-cash process, is a sequence of steps taken by a company to identify, acquire, and close a customer. Sales processes can consist of different phases: They range from addressing the customer through the preparation and presentation of the offer to the final negotiation and the conclusion of a contract. By optimizing sales processes, companies can typically, reduce their sales costs, increase their sales volumes and improve customer satisfaction.
Webinar Sales Management
Efficient Sales Management in Salesforce
Customer relationship management plays a central role today – be it to obtain a 360-degree view of your customers, to enable customer-centric processes, to shorten response times or to increase the ability of employees to provide information.
For this reason, companies today have a CRM system in place and often rely on the world’s leading provider of CRM software from the cloud: Salesforce. And what should definitely not be missing from your Salesforce? Exactly! All information and processes around your documents.
Start the webinar with just one click on the video and watch it for free.
How are business processes structured?
Business processes consist of a series of steps that are performed in a specific order to achieve a given goal. The steps of a business process are usually interconnected and enable the organization to perform a task or business process effectively and efficiently.
A typical business process basically starts with an event that triggers the business process. An enquiry or request. After all the information required for the process (input data) has been provided, the actual activities of the business process required to achieve the goal are identified. Decision points exist within or between the process activities, i.e., these are points in the process at which certain decisions have to be made, determining the further course of the business process. A comprehensive audit trail is generated during each stage of the process, allowing for reporting and analysis throughout the whole transaction. Business processes can be both manual or automated and additionally linked to other business processes, reflecting a larger business activity.
The following figure summarizes the basic structure of a business process:
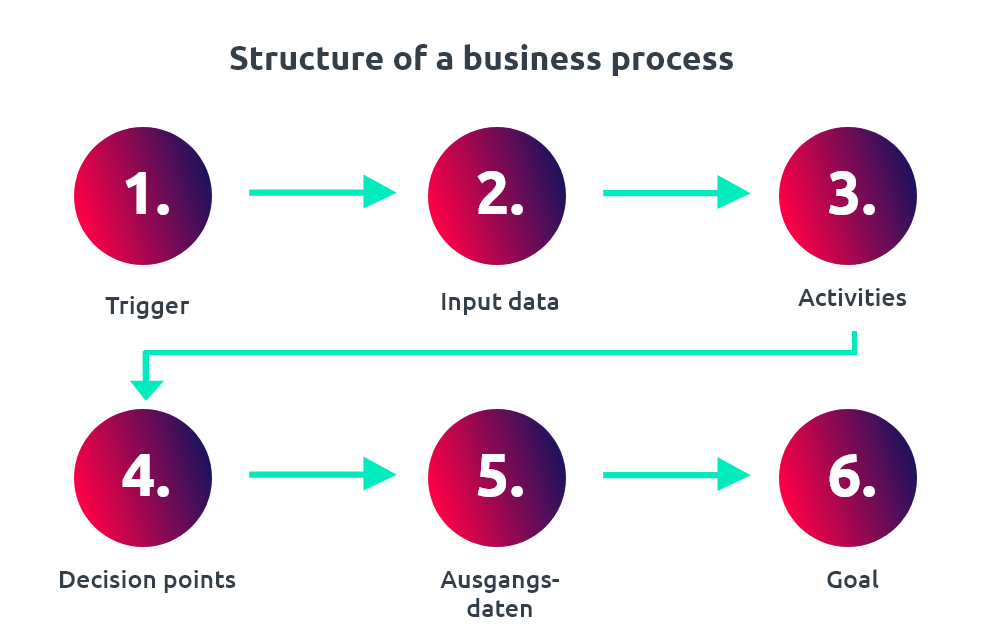
- Trigger: An event or activity that triggers the business process.
- Input data: The information required for the business process.
- Activities: The actual steps of the business process that must be performed to achieve the goal.
- Decision points: Points in the process where decisions must be made.
- Output data: The information that is generated after the business process has been completed.
- Goal: The ultimate goal of the business process to be achieved.
Business process chain
The process chain refers to the connection between the individual activities within a business process. A process chain shows the dependencies and flow of activities in a business process and enables the effectiveness and efficiency of a process to be evaluated and optimized. Therefore, the process chain represents an important link for monitoring, control and optimization between the business process activities within a company.
Business process map
A process map graphically shows the individual steps and activities of a business process. It is a visual tool that provides an overview of a process and its dependencies, as well as its interactions with other processes. The process map is an important part of process management and helps with the analysis and optimization of business processes. In short: A process map is an instrument for depicting a business process and its relationships.
What are the benefits of business processes?
Business processes offer companies numerous advantages that extend to different areas. Some of the key benefits of business processes are:
increase in efficiency
Business processes contribute to the standardization and automation of work processes in the company. This allows processes to be designed faster, more cost-effectively and with fewer errors. The clear structuring of tasks and responsibilities makes it possible to use resources in a more targeted manner and thus, increase the efficiency of the company.
Cost cutting
Business processes can lead to significant cost savings in companies. By analysing and optimizing processes, unnecessary work steps can be eliminated, double entries avoided and the process speed increased. In digital invoice processing as an example, companies can achieve significant cost savings by automating processes such as checking invoices for duplicates. In addition, compliance and the avoidance of errors, e.g. through automatic account assignment, can contribute to cost reduction.
Transparency and traceability
Business processes create a clear overview of what is happening in the company and ensure that all activities are in line with the company’s goals. This enables those responsible to keep track of the current state of affairs at all times and to ensure compliance with standards and regulations, such as local GDPR. Business process traceability also makes it easier to identify errors and resolve issues.
Customer satisfaction
Business processes aligned with customer needs and expectations help increase customer satisfaction. By automating processes, companies can shorten their processing times and react more quickly to customer inquiries and needs. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and better customer loyalty.
Flexibility
Companies that implement efficient and well-designed business processes can gain a competitive advantage. They are able to produce and deliver products and services faster and more cheaply than their competitors. By continuously optimizing business processes, companies can also react more flexibly to changes in the market and strengthen their competitive position.
Fast training
Business processes can help speed up and simplify the onboarding of new employees. When a company has clearly defined business processes, a new employee can quickly understand how certain processes within the company work. This allows new employees to integrate more quickly and start their work faster and more effectively.
Business process management
Business process management (BPM) describes an integrated system of organization, management and controlling. It is used for the targeted control, design and optimization of business processes in companies. The overarching goal of business process management is the effective and efficient design of a comprehensive process landscape. The introduction of BPM basically includes the following steps:
1. Process analysis and planning
The first step in introducing BPM includes the analysis of the existing business processes and process planning. First of all, all relevant business processes must be identified and documented — for example with the help of diagrams or text descriptions. Process maps can be used to provide a visual representation of the process, which provides an overview of all process steps and the actors involved. These form the basis for identifying weak points or bottlenecks. A generally recognized and tried and tested technique for strategic planning is the SWOT analysis, which is used in particular to determine the current position and to develop suitable strategies.
2. Business Process Optimization
Business process optimization is an important part of business process management and deals with the improvement of the previously analysed processes. By optimizing the existing business processes, weaknesses can be uncovered and eliminated before the business process model is further developed. Key business process optimization techniques include:
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR): A method for radically redesigning business processes to improve their effectiveness and efficiency.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Systematic approach aimed at integrating quality into all aspects of the organization, including business processes.
- Balanced Scorecard: Strategic management tool that measures organizational performance from financial, customer, internal process, along with learning and growth perspectives. It can help to improve the alignment of business processes with the company’s overall strategy.
- Continuous improvement process (CIP): Method for systematically improving business processes by constantly identifying and eliminating weak points.
- Kaizen: Japanese philosophy of continuous improvement aimed at achieving constant improvements in business processes in small steps.
- Lean Management: A method of streamlining business processes aimed at increasing efficiency, minimizing waste and improving quality.
3. Business Process Modelling
The process modelling builds on the optimised business processes and supports the long-term orientation of the company. The Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a commonly used technique. It is a modelling language that enables a standardised representation of business processes. In addition to BPMN, the technologies that support users in business process modelling include UML (Unified Modelling Language), EPC (Event-driven Process Chain), DFD (Data Flow Diagram) and IDEF (Integrated Definition).
4. Workflow Management
Following the business process modelling, the actual implementation of the previously optimised processes follows. Workflow management (WFM) plays a central role here. Business process management and workflow management are often mistakenly used as synonyms. While GPM aims to manage, control and optimise business processes, WFM specifically refers to the automation of tasks and activities within a business process. Workflow management is therefore a subset of BPM and deals with the technical implementation of business processes.
Workflow management is an important step in introducing business process management in companies, as it automates the implementation of the identified processes and enables continuous monitoring and optimisation of these processes.
5. Process monitoring and controlling
The optimised and implemented business processes are monitored via process monitoring. It allows companies to uncover weaknesses in the process and take action to improve efficiency. The objectives of the monitoring are to ensure stable and effective process performance, to identify potential for improvement and to meet service level agreements (SLAs) and compliance requirements.
Various methods are available for carrying out the monitoring, such as:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): KPIs are used to set target values for key performance indicators that make it possible to measure and monitor the performance of business processes.
- Business Activity Monitoring (BAM): BAM enables real-time monitoring of processes and analysis of events and data in order to be able to react quickly to changes.
- Business Process Intelligence (BPI): BPI is a method used to analyse and visualise process data to understand and improve process performance.
- Risk management: Risk management is used to identify, analyse and evaluate risks in business processes in order to minimise risks and ensure the stability of processes.
Digitization of business processes
The digitization of business processes is an important part of business process management. By implementing digital systems and automating processes, companies increase the efficiency of their business processes and benefit in particular from error minimization and cost savings.
Automate business processes with a DMS
A document management system (DMS) helps companies automate their business processes by replacing the manual processing of documents and information with automated workflows and processes. The DMS can capture, classify, index and automatically route documents to the right people or systems. For example, invoices can be automatically captured and forwarded to accounting, while contracts are automatically sent to the legal department or management team. By automating business processes, companies can save time and money, reduce errors, and improve efficiency and transparency.

DMS White paper
Digital document management explained
What should a document management software be able to do? What are the benefits of implementing it? Find out in a 20-page whitepaper.
Contents of the whitepaper:
- Understanding digital document management
- The 7 key functions overview
- Step-by-step guide to implementing a DMS
What advantages does a document management system offer for business processes?
Digitization of documents
By digitizing documents, they can be saved and edited directly in the DMS. This ensures version and revision control, whilst ensuring access and permission security. Ultimately saving time and money, that would otherwise be incurred for manual processing and physical storage of the documents.
Automated workflows
Automated workflows can be created with a DMS. This means that certain steps of a business process are executed automatically once specific conditions are met. For example, a document can be released automatically as soon as it has been checked and approved by all the necessary authorized people.
Integration of systems
A DMS can be integrated into existing IT systems such as ERP systems. This allows information to be exchanged automatically and processes to be optimized.
Electronic Signatures
A DMS offers the possibility of signing documents with a digital signature in a legally secure manner. This saves time and money by eliminating the need to print, sign, scan and mail the document.
Automated archiving
The introduction of a DMS enables digital document archiving within business processes. This means that they are automatically saved in the right version and in the right place. In particular, the requirements for revision security are met by a document management system.
Cloud connection
The cloud migration of a DMS offers numerous advantages for the business process management of companies. Because the DMS is hosted in the cloud, users can access and control the business processes from anywhere, as long as they have an internet connection.
Digital business processes with d.velop documents
The introduction and optimization of business processes is a challenge for many companies. d.velop documents supports companies in the implementation of their business process management. The solution offers cost savings, legal certainty, whilst increasing efficiency and many other benefits.
Questions about business processes?
We have the answers.
The goal of business process management is to optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes. This involves the analysis, modeling, implementation, and monitoring of business processes to ensure they run efficiently and effectively.
To achieve the goal of optimizing business processes, a thorough analysis of the processes needs to be conducted. This involves identifying weaknesses and areas for improvement. Various techniques can be employed to optimize the processes, such as Business Process Reengineering, Total Quality Management, Lean Management, or Kaizen. These techniques aim to streamline processes, eliminate waste, enhance quality, and continuously improve efficiency. By applying these appropriate optimization techniques, organizations can achieve significant improvements in their business processes.
The digitization of business processes is enabled by the use of a Document Management System (DMS), which supports automated document processing and electronic communication. A DMS offers features such as electronic archiving, workflow management, monitoring of business processes, and integration with other business applications.
Business process management and workflow management are closely related, but there is a difference between them. Business process management encompasses the analysis, optimization, and monitoring of business processes, while workflow management focuses on the automation and control of workflows. A workflow management system is a type of business process management system that specializes in managing workflows.
Business processes play a crucial role in the digitalization of companies. The goal of digital transformation is to improve and automate existing business processes through the use of digital technologies. By digitally mapping business processes, efficiency is enhanced, sources of errors are minimized, and ultimately costs are reduced. Companies can therefore respond to market changes more quickly and flexibly, and increase customer satisfaction.
In order to make business processes legally compliant, companies should consider legal requirements and internal regulations. Clear documentation, tracking of changes, access restrictions, and regular employee training can help meet legal requirements and minimize compliance risks.
Business processes can be modeled using modeling techniques such as BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) or UML (Unified Modeling Language). In this process, the individual steps and connections between the steps are represented in a graphical representation.
Software Demo
Get to know the d.velop software
Request your personalised live demo of the d.velop software with just a few clicks. Get a live demonstration of the software and ask your questions directly. Simply fill in the form and we will get back to you.
