The XML signature is an indispensable tool in the modern digital world that ensures the authenticity and integrity of XML data. In this blog article, you will learn how to sign an XML file to ensure that the data is unaltered and from a trusted source. We will explain the necessary steps and best practices to create a secure and reliable XML signature. Whether you work in IT, e-commerce or the public sector, knowing about XML signatures will help you increase the security of your digital documents and ensure compliance with legal requirements. Dive into the world of XML signatures and learn how to effectively protect your XML data.
Essential Knowledge Before Implementing XML Signatures
What is the XML format?
The XML format allows users to save data in a structure that can be read by machines (unlike the classic PDF). The term “XML” stands for “Extensible Markup Language”, which translates as “extensible markup language”. The XML format is a standard that enables the exchange of structured information between applications. As an XML file is formatted as a text document, it can be displayed, read and edited using a simple text editor.
What is an XML file?
An XML file can be regarded as a text-based database. The XML file uses user-defined tags such as “<H1>” and has now replaced the HTML file as the standard method for saving and transferring between programmes.
What is an XML signature?
An XML signature is a digital signature format that has been specially developed for XML data. It is a specification for the use of digital signatures in XML format. It enables the authentication and integrity of XML documents and is often used in web services and other XML-based applications. Depending on the type of document being signed, a specific signature format – the “language” of the signature, so to speak – is used. In the case of an XML file, the signature format is usually XAdES. The formats are defined in international specifications.
What XML signature methods are there?
There are two signature methods, the “internal” and the “external” signature. With the internal signature, the signature is applied directly to the XML document. With the external signature, on the other hand, it is created in a separate signature file. This means that there is an original file and a signature file.
How to sign an XML with d.velop sign
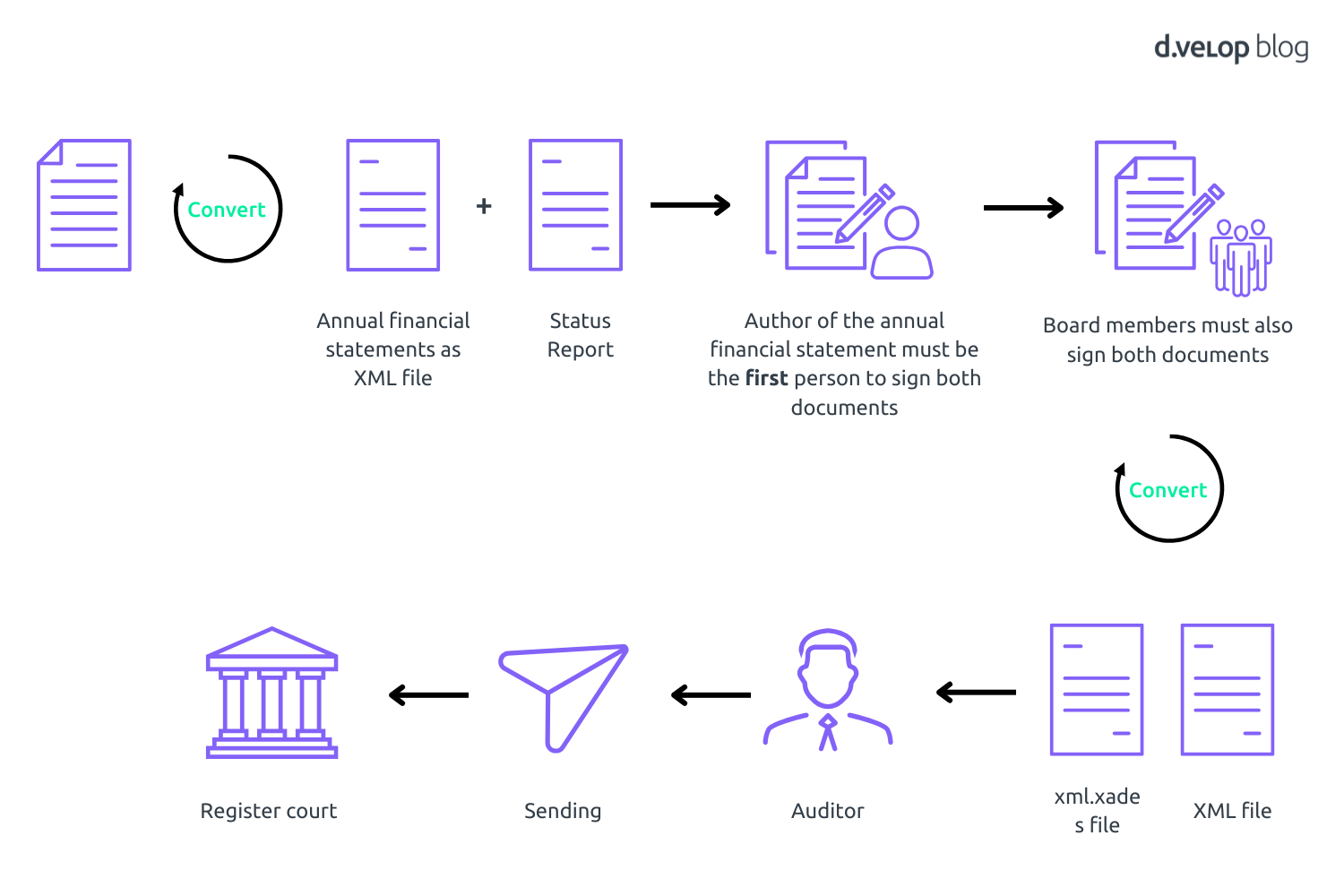
The document – in this case an annual financial statement – must be created in XML format. This is how you proceed step-by-step to sign the XML:
- The author signs the XML document first
- All authorised signatories then sign with an external signature. The current signature file can be extended or a signature file can be created for each signatory.
- In the international area, attention must be paid to the corresponding ending of the XML file. The file name of the signature file must have the file extension XAdES for Poland, for example. If this is not the case, the signature file must be renamed manually.
- Once all obligated persons have signed, the document can be sent to the auditor. The auditor receives the signed documents and checks their content for correctness.
- As soon as the auditor has confirmed the documents, they are ready to be sent to the registry court. To do this, the company must register online. In the case study, this is possible for Polish companies on the government website.
- The qualified signed XML file can now be uploaded.
Advantages of the XML signature with d.velop sign
The XML signature offers numerous advantages for companies and organisations, making it an indispensable tool in the digital working world. Here is an overview of the most important advantages:
- Authentication: The XML signature with d.velop sign ensures that the document originates from a trustworthy source.
- Interoperability: Standardised and widely used, which facilitates integration into various systems.
- Security: Utilises strong cryptographic algorithms to ensure data integrity and authenticity.
- Cost efficiency: By digitising and electronically signing documents, companies can significantly reduce paper costs and administrative effort.
The XML signature with d.velop sign offers a secure, flexible and cost-efficient solution for securing XML data. Its ability to guarantee authenticity and integrity makes it an important component of modern IT infrastructures and applications.
How the signature certificate protects an XML file from changes
Definition signature certificate
A signature certificate is an electronic document that confirms the identity of the signatory and the validity of a digital signature. It consists of a public key issued by a certification authority and further information about the signatory.
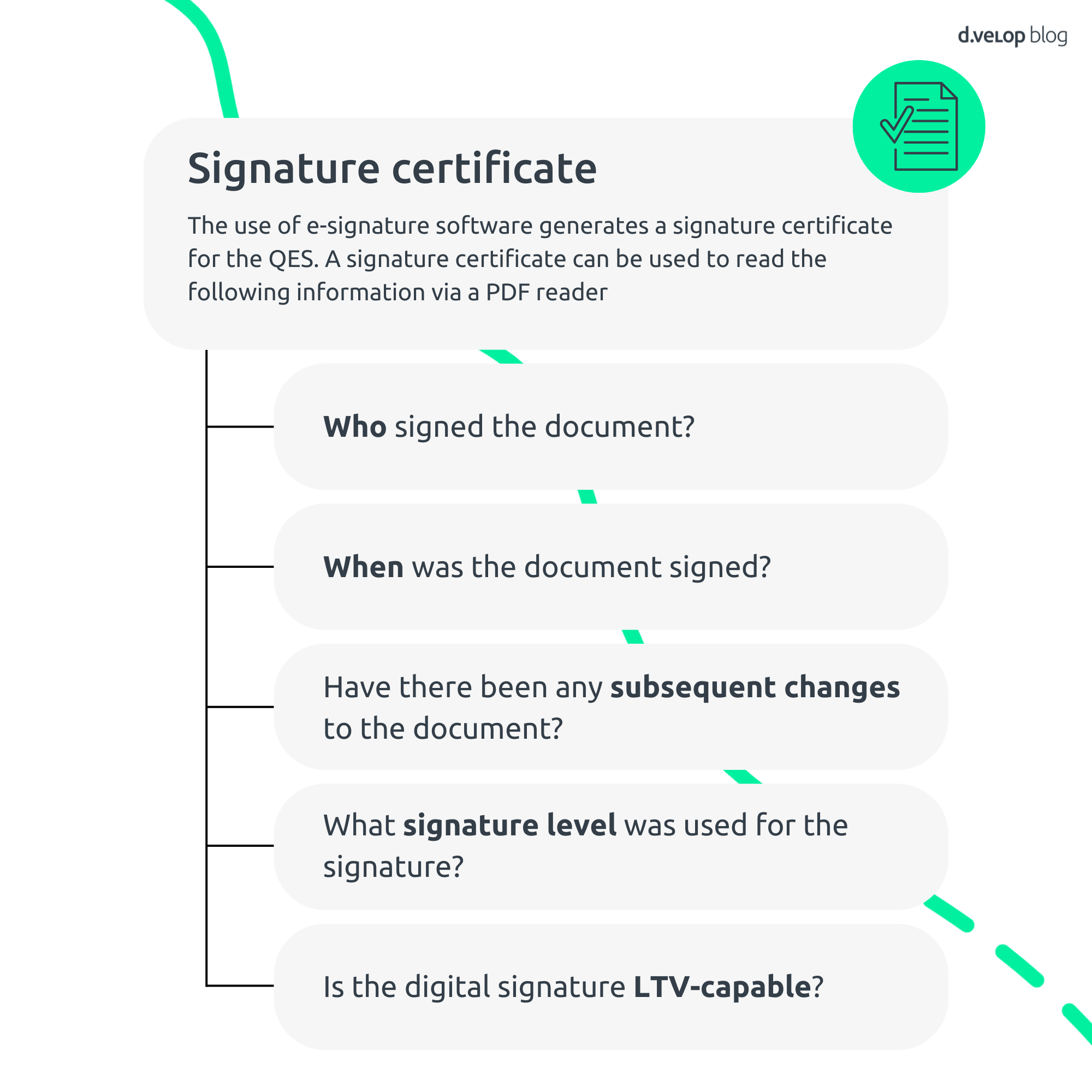
A signature certificate is issued by a recognised certification authority, also known as a trust service provider, which assigns a key pair consisting of a private key and a matching public key to a person or organisation. A signature certificate is issued when a person signs a document with an advanced electronic signature (AES) or qualified electronic signature (QES). The detailed requirements for these signature levels are set out in the European eIDAS Regulation. The signature certificate issued is publicly accessible. The following stored information can be read using a PDF reader, for example:
- Identity of the signatory: Who signed the document?
- Date of signature: When was the document signed?
- Integrity protection: Were there any subsequent changes to the document?
- Security level: What signature level was used to sign the document?
- Validation and certification authority: Who issued the certificate and is it LTV-capable?
When is an XML signature no longer valid?
For external signatures, you can choose whether to create an additional signature file or extend or replace the existing one. In principle, it makes sense to create a separate signature file for each signatory. If changes are made to the original document after the XML signature, the signature is ‘broken’ and is no longer valid.
Increasing areas of application for the XML signature
The XML signature has established itself as a versatile and secure tool that is used in a wide range of industries and applications. As digitalisation progresses and data security becomes increasingly important, the areas of application are constantly expanding. Here are some of the most important areas in which XML signatures are increasingly being used:
E-government and public administration
- Digital government services: securing electronic documents and forms.
- E-voting: Ensuring the integrity and authenticity of electronic votes.
- E-legislation: Digital signature of legal documents and ordinances.
Healthcare
- Electronic patient records: Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of health data.
- E-prescriptions: Authentication and traceability of electronic prescriptions
- Telemedicine: Ensuring the integrity of medical reports and diagnoses.
Financial services
- Online banking: Securing transactions and communication between banks and customers.
- E-contracts: Digital signature of financial contracts and agreements.
- Insurance: Authentication of claims notifications and policies.
E-commerce and trade
- Electronic invoices: Ensuring the authenticity and integrity of e-invoices.
- Conclusion of contracts: Digital signature of sales contracts and agreements.
- Supply chain management: Securing documents and data along the supply chain.
Education and research
- E-learning: authentication of certificates and degrees.
- Research documents: Ensuring the integrity of research reports and publications.
- Student administration: Digital signature of registrations and certificates.
Corporate communication
- Internal documents: Securing internal reports, protocols and guidelines.
- Contract management: Digital signature of internal and external contracts.
- Compliance: Ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
The XML signature with d.velop sign is being used in more and more areas, as it offers a secure and flexible solution for securing data. The focus is always on its ability to guarantee authenticity and integrity.
Example Poland: Submit annual financial statements digitally via XML signature
The annual financial statements must be submitted as an XML file and must be digitally signed in this format – all other forms are not permitted. The signature format is XAdES. The new regulation is intended to speed up and simplify the disclosure of financial statements and make the data accessible to everyone.
The management report must also be prepared and signed in electronic form. It should be noted that the annual financial statements and management report have the same signature date. According to our information, it is not possible to submit the management report at a later date. All managing directors and authorised signatories (e.g. the management board) are obliged to sign both documents.
The annual financial statements were just the beginning of the XML signature
Since 2020, all applications – not just annual financial statements – must be submitted digitally in the register procedure using the qualified electronic signature or the ePUAP signature. The eIDAS-compliant remote signature makes it possible to execute signatures from anywhere and at any time, as well as a qualified electronic signature. No hardware components such as signature pads or TAN generators are required for the signature process. Due to its simple handling, it is often used by European companies based in Poland.
XML signature: A standardised procedure for more security in the digital working world
The XML signature is an indispensable tool for securing XML data in a wide range of applications. Its ability to guarantee authenticity and integrity makes it an important component of modern IT infrastructures.
💻Book Software Demo
Experience the power of d.velop’s software with a personalised live demo, easily requested with just a few clicks. Watch as the software comes to life before your eyes and ask any questions you may have in real-time.
