“In reality, a company is a continuous process, an uninterrupted chain of performance.” With this quote, Fritz Nordsieck, a representative of business organisation theory, pointed out the importance of workflow management and business processes in 1932. What is taken for granted today was by no means a given 90 years ago. For a long time, business administration focused on the mostly hierarchical organisational structure, before Nordsieck shifted the focus to business process analysis and optimisation.
Despite everything, in times of digitalisation we have far exceeded these findings. It has long been no longer a question of simply aligning the company with business processes, but also of mapping them electronically and as standardised as possible. And this is where workflows come into play. In this article we address the question “What is workflow management?” and provide the most important information for getting started with the d.velop process studio.
What does workflow mean?
Definition: What is meant by workflow?
A workflow or DMS workflow is primarily used for process automation, i.e. the automation of a business process. It is a flow chart that specifies which work steps are required for the business process and who exactly carries them out. The workflow has a clearly defined start point, process and end point.
What is workflow software?
With the help of workflow software, analog business processes are digitised and automated using IT. Workflow software forms the basis for a workflow management system and thus for the control of modelled workflows.
What is workflow management?
Workflow management encompasses the entire process of planning, modeling, controlling and analysing workflows. The goal of workflow management is to design the optimal workflow.
Workflow Management and Business Process Modeling
Workflow management and business process modeling are closely related but are two different concepts that are often used in conjunction with each other.
- Business Process Modeling: Business Process Modeling refers to the process of creating models that represent the various steps or activities performed in a business process. These models can take various forms, including flowcharts, BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) diagrams, or other graphical representations. The main goal of business process modeling is to visually represent the process to provide a better understanding of its structure, logic, and potential areas for improvement.
- Workflow Management : Workflow management refers to the management and automation of business processes. It involves defining, executing and monitoring workflows within an organisation. These workflows can be based on the business process models created during BPM. Workflow management systems (WMS) are often used to control and optimise the flow of tasks, information and documents within an organisation.
Business process modelling and workflow management can be considered as two phases of the same process. First, the business processes are modelled to understand and document them, and then these models are translated into workflows and managed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of these processes.
Workflow Management: How does a workflow differ from a classic business process?
In terms of the level of detail, a workflow is clearly different from a business process. For a better understanding, let’s first explain what a business process actually is:
Definition of business process
A business process consists of many small work steps in order to achieve a defined goal within a company with maximum efficiency.
Business process example: Onboarding a new customer
- Check whether the customer data is stored in the system
- Request missing customer data from the customer
- Store customer data digitally
- Digital recording of the signed contract
- Filing the contract in the customer folder
- Brief project-related employees about the customer: Coordinate and set a briefing date
- Contact customers for the kick-off meeting
What is meant by workflow and business process?
While the business process is primarily focused on business management aspects and the representation of the sequence of work steps in a business process, a workflow aims at the detailed technical description of the work steps. The business process therefore describes “what” is to be done on a technical and conceptual level and, in contrast to the workflow, is therefore of great importance for the strategic orientation as a whole. The level of detail is, however, much coarser than that of a workflow.
Workflow makes process automation possible
A workflow, on the other hand, describes not only the “what” but also the “who”. The workflow therefore reads more like a precise work instruction. It must be so detailed and precise that the workflow can support an employee in the work sequence, or the processing can even be completely automated. A workflow is therefore very important for the precise coordination of various business processes.
Not to be confused: Workflow Management and Business Process Management (BPM)
The terms Business Process Management (BPM) and Workflow Management are often used synonymously, but there are significant differences.
Workflow management focuses on the analysis and optimisation of individual business processes in detail, as well as on targeted coordination and organisation. Business process management takes a much more comprehensive look at business processes as part of a business process analysis and focuses on targeted integration into the company and strategic orientation.
Workflow Management Systems: More than just task management
Workflow management goes far beyond simple task management. Workflow management systems enable business processes to be completely adapted to the individual needs of the company. While task management systems are usually limited to individual organisational units and only allow strict business processes without any deviations, a workflow management system offers significantly more flexibility across companies and departments.
Workflow Management: Difference between structured and semi-structured processes
Not all business processes are the same. Not all workflows are the same. In theory, business processes can be roughly divided into structured and semi-structured processes. If this is applied to workflow management, structured business processes are referred to as normative workflows and semi-structured business processes are referred to as adaptive workflows or process management.
Fixed process vs. information-based process
The following graphic illustrates the key difference between workflows for structured business processes and workflows for semi-structured business processes. In a workflow for a structured business process, the work step defines the user’s activity. The process is predictable and has a clearly defined sequence. In a workflow for semi-structured business processes , on the other hand, the user uses his or her experience to select the sub-activities that are necessary to optimally handle the process. Since these workflows are not necessarily predictable, the user individually determines the next process step based on the information available to him or her.
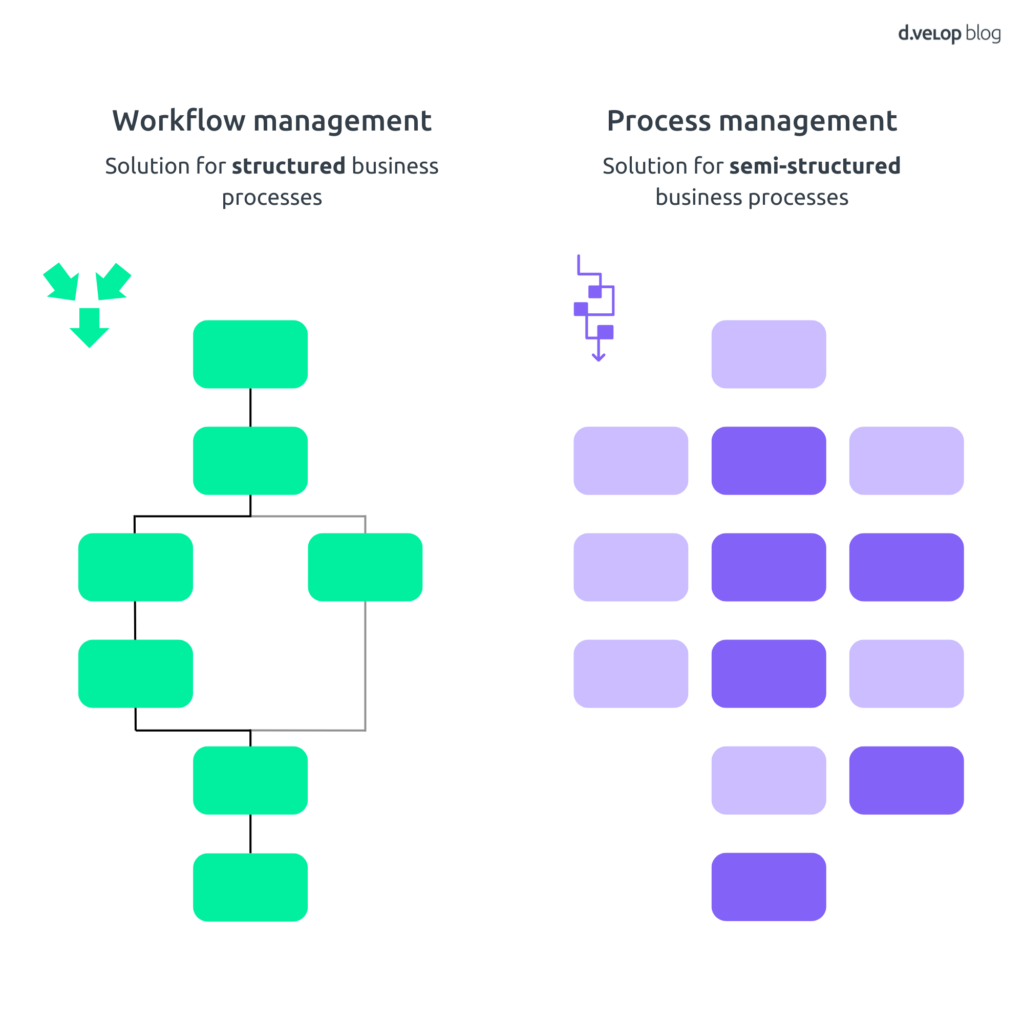
In practice, it is often difficult to make a clear distinction between workflow management and process management. Either both can be used equally, or the individual phases merge smoothly into one another within a business process.
What types of workflows and processes exist in companies?
Business processes in companies are diverse. The possibilities for supporting these business processes electronically with workflows are just as diverse. The possibility of digitally mapping business processes using workflow software arises in basically every department – regardless of whether it is in production, sales or purchasing. Workflows are also used in companies in every industry, be it in mechanical engineering, the automotive industry, the chemical industry or in retail. Below you will find a list of the most common electronic workflow examples in companies:
- Inbox distribution
- Incoming invoice processing
- Complaints management
- Approval workflows
- Purchase requisition (SAP BANF)
- Custom-made request
- Quality management
- Master data processes
- Personnel and applicant management
- Holiday requests
Workflow management, business processes and BPM – differences at a glance
- Workflow: a clearly defined schedule for successive work steps
- Workflow Management: Planning, modeling, controlling and analysing workflows
- Workflow software: IT-supported digitisation and automation of workflows
- Workflow Management System: Complete adaptation of business processes to the individual needs of the company
- Business process: Analysis, optimisation and representation of the sequence of work steps to achieve a defined goal – less detailed than workflow, as the focus is on strategic orientation
- Business Process Management (BPM): Strategic and targeted integration of business processes in the company
- Process management: No predefined workflows as in workflow management, employee chooses next process step individually based on personal experience
Workflow Management: Examples from everyday work
1. Approval workflow for vacation requests
- If vacation is desired, each employee must create a digital vacation request at least three months before the desired period and send it to the responsible human resources manager
- The responsible HR manager takes note of the vacation request and checks the staffing of the department for the specified period in the vacation calendar
- Rule: At least half of the department must be present at all times
- According to the rule, the HR manager must confirm or reject the vacation request by email within 7 working days
- The vacation period of the confirmed vacation request must be entered immediately in the vacation calendar by the responsible human resources manager
The workflow example shown makes it clear that a workflow represents a clearly defined work sequence for the employees involved. The workflow thus enables precise coordination of successive work processes.
2. Travel expense accounting as an example of a structured business process
A simple and well-known workflow example is travel expense accounting. Travel expense accounting is a structured business process that is very similar in many companies. The process is predictable and there is a clear start and end point. Travel expense accounting therefore offers the perfect conditions for digitisation via a workflow. The typical steps of a travel expense workflow are as follows:
- Recording of travel expenses by the employee
- Submitting the application to the supervisor
- Approval/rejection of travel expense report
- If rejected: Inform employee with request for adjustment
- Upon approval: automatic creation of a travel expense receipt
- Digitise and archive receipts
- Hand over the receipt to the HR department and settle any outstanding amounts
We have already described in more detail in one of our blog articles what a digital SAP travel expense report can look like.
What are the benefits of workflow management?
Regardless of whether it is workflow management or process management – supporting business processes with the help of workflows offers companies many advantages and usually has a positive effect on various areas immediately after implementation:
- Increase efficiency: Increase efficiency and reduce lead times.
- Transparency: Status and progress of tasks and processes immediately visible
- Standardisation: Consistent execution of tasks leads to higher quality
- Compliance: Adhering to regulations and guidelines minimises risks
- Cost savings: reduction of manual and time-consuming activities
- Flexibility: Processes can be adapted and scaled as needed
- Better decision making: Real-time data and analytics support decision making
- Customer satisfaction: More efficient processes and better communication
- Productivity: Better structured workflows lead to increased productivity
- Data: Better management and use of data through better flow of information
- Communication: Automation and standardisation of communication processes
- Collaboration: Better teamwork through transparent assignment of tasks
- Avoiding media disruptions : flow of information between departments and systems
- Minimise sources of error: improve accuracy and reliability
- Improved process quality: standardised procedures and control mechanisms
- Flowcharts: visual representation of business processes for more effective analysis
Workflow Management System: Work faster and more productively with workflow software
Document management system (DMS) and workflow software
Business processes usually involve a wide variety of documents, such as invoices, contracts or order confirmations. Each of these documents is linked to a workflow, so there is a crucial connection between workflow management and document management.
Document management systems (DMS) enable optimal control of documents through the respective business processes in the company. Whether it is the automated filing and distribution of digital documents or automatic review and approval workflows – a DMS with integrated workflow software makes the company more productive in all respects.
Advantages of an SAP workflow
An SAP workflow enables the efficient and fully automated processing of recurring workflows through the intelligent coordination of process steps. We explain the specific advantages of an SAP workflow and how the introduction of an SAP workflow works in the blog post SAP Business Workflow .
Workflow in SharePoint Online
The greatest strength of SharePoint Online lies in efficient and transparent collaboration. Whether in the office, via remote work or in the home office – workflows in SharePoint create numerous opportunities for collaborative work with documents, lists and libraries. We explain what types of workflows there are in SharePoint and what advantages they bring in the blog post on the topic of SharePoint workflows in Microsoft 365 .
Workflow management as the heart of every ECM software
Workflows are the heart of the classic ECM model. And even in new approaches, such as Enterprise Content Services, it will be unavoidable for companies to process captured documents using workflows. d.velop not only provides the pure software solution, but also the necessary analysis and advice. As part of a personal workshop, we examine current processes with companies, uncover optimisation potential and sources of error, and develop effective ways to optimise business processes.
Workflow management in practice: Experience the d.velop process studio now
Book your individual software demo for the d.velop process studio in our document management system with just a few clicks. Let our experts demonstrate the software live and ask your questions directly.
Frequently asked questions and answers about workflow management
What is workflow?
A workflow or DMS workflow is used to automate business processes . It is a plan that defines the required work steps and responsibilities. The workflow has a clear start, process and completion.
What is workflow software?
Workflow software enables the digital and automated transformation of analog business processes through IT support. It forms the basis for a workflow management system that enables the control of modelled workflows.
What is workflow management?
Workflow management includes the planning, modeling, control and analysis of workflows. It aims to design the optimal workflow.
How does a workflow differ from a classic business process?
The business process focuses mainly on business aspects and the representation of the sequence of work steps. In contrast, a workflow aims to describe the work steps in technical detail.
