When it comes to digitising your SAP system, well-maintained master data is of great relevance. In this blog article you will find out a definition of SAP master data, the importance it has for your company and how it contributes to digitisation.
What is SAP master data?
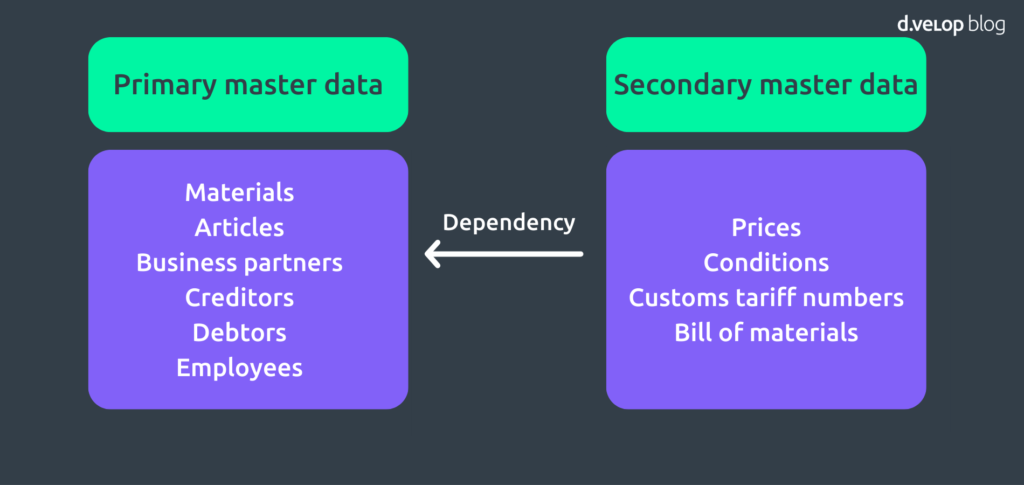
Master data is operationally relevant data that rarely if ever changes. This includes, for example, information about materials and articles, business partners such as vendors and debtors, and employees. SAP master data is recorded in the SAP system and is available to all applications and the respective authorised SAP users.
In master data, a distinction is made between primary and secondary master data. The already mentioned data records materials, articles, business partners and employees are part of the primary master data. It is characteristic here that this information can stand alone. The secondary master data, on the other hand, usually only makes sense in connection with other data records (e.g., primary master data). Secondary master data is information such as prices, conditions, customs tariff numbers and parts lists. Prices, for example, are hardly meaningful on their own. However, if these are related to the primary master data such as material or article, the SAP system can work with them.
The exact opposite of the master data is the transaction data. They change regularly and are only temporarily related to the master data. Examples of this are orders from customers or stocks of raw materials.
How important is SAP master data for companies?
Master data is essential for the operation and use of the SAP system. They are required to control operational business processes, are a prerequisite for data evaluation and serve as the basis for company decisions. Achieving and maintaining a high quality of SAP master data is not easy but offers enormous advantages. They enable transparent and efficient business processes and reduce the working time for corresponding processes by 5% on average.
Disadvantages of low master data quality, on the other hand, are significant problems along the value chain, which are often associated with high costs. A scientific study by the RWTH Aachen has shown that poor master data quality in the manufacturing industry leads to more queries, longer throughput times, additional costs in operational processes and poor process quality. These occur most in production planning, sales and order processing, materials management or warehouse management.
Let’s look at some examples of this
Incorrect customer master data
Many companies only send their SAP outgoing invoices to their customers by e-mail. If incorrect or outdated e-mail addresses are stored in the SAP customer master data, the invoice will not reach the customer. This leads to increased coordination effort, in which many different people are involved, time and money are lost and in the worst case, the relationship with the customer suffers.
Incorrect information in article master data
If picking slips are created in logistics, based on incorrect weights or dimensions from the SAP article master data, the goods issue is delayed. Deliveries that have been put together incorrectly have to be processed several times and costs can arise due to increased waiting times for the forwarding agents.
Incomplete raw material master data
If raw materials are created incompletely in the SAP system, this leads to errors in the corresponding production orders. If, for example, necessary properties such as kosher or halal are not stored for food, the production orders cannot be carried out until it is clarified whether these certifications actually do not exist or have simply not been maintained in the SAP system.
Inaccurate database for evaluations
SAP master data form the basis for company-wide analyses and data evaluations. These evaluations are often used for strategic company decisions. An inaccurate or faulty database thus leads to wrong strategic decisions, which can have far more serious consequences than loss of time and money.
These are certainly just a few examples of the many problems and negative consequences of poor SAP master data quality. They clearly show that high and sustainable master data quality, is an essential business factor for corporate success.
The importance of SAP master data for digitisation
According to the Lünendonk® study from 2016, good master data quality is fundamental to digitisation in a company. Specifically, it describes that digital business models are only possible if companies have their master data under control. Consequently, companies who do not have their master data under control, must review their data control processes, prior to starting with digital business models.
A good example of this is the digital processing of incoming invoices. With d.velop invoices for SAP, the SAP master data plays a major role in order to be able to use as much integration and automation as possible. Digital incoming invoices are classified in the invoice reader. The invoice reader recognises the supplier, his address and other information such as IBAN or tax number. By comparing this data with the SAP master data, the invoice can be clearly assigned to the supplier. If it is an MM invoice, i.e., with an order reference, the item data of the invoice can be read out and also compared with the SAP system. Either a list of the open orders for the vendor can be used, or if the goods receipt has already been posted, a list of the open deliveries.
In the case of cost calculations, so-called FI invoices, it is often difficult to find the right clerk. This step can also be simplified by using the SAP master data. The clerk stored in the SAP master data is selected automatically so that the invoice workflow can start immediately.
So, you can see that in our example of the digital processing of incoming invoices with d.velop invoices for SAP, the interaction between the software and the SAP master data is of great importance. If a comparison with the SAP master data is not possible or if the quality is too low, manual intervention is necessary in many cases, so that the advantage of automation is almost eliminated and cost of processing increased.
Would you like to see what automated processing of incoming invoices can look like in your company?
