You are now wondering what SAP FI cost accounting has to do with AI? The answer is quite simple and we will clarify it in the next few paragraphs. Let’s start by looking at each term separately.
What is SAP FI?
SAP developed the Financials (FI) module for financial accounting. SAP’s FI module is one of the oldest and most widely used modules in the SAP world. It covers all business processes in the area of finance and accounting. This includes, among other things, accounts receivable and accounts payable as well as general ledger and subledger accounting.
SAP FI is often referred to together with SAP CO as SAP FICO, as the two systems are closely linked.
What is SAP FI cost accounting?
SAP FI cost accounting is mainly known to employees in accounting who map their financial processes in SAP ERP. SAP FI cost accounting includes ordered goods or services for which there is no purchase order in the SAP ERP system. These invoices can, for example, contain individual items such as office materials or represent complex settlements for countless telephone and cell phone connections of the most varied kinds. An invoice without a purchase order reference always means more work for the employees in the accounting department during processing.
What does SAP FI cost accounting have to do with artificial intelligence?
AI stands for artificial intelligence. As already mentioned, SAP FI cost accounting requires more effort to process due to the lack of a purchase order reference. But why is this the case? Invoices with purchase order reference, so-called MM invoices, can be compared with the SAP master data. This automatically results in the corresponding agent and account assignment data for the invoices. This automation is initially missing for SAP FI cost invoices. In the worst case, the invoices must always be assigned manually. Depending on whether the account assignment is carried out by experienced employees or by new employees, more or less time is required for this work step. But I think we can all agree that manual account assignment of SAP FI cost invoices involves a lot of effort that needs to be minimized. And this is exactly where AI can support.
What does the AI do?
The AI “learns” from historical experience values of already processed cost invoices. The OCR texts read from the invoices are evaluated and related to the actual SAP posting and the information contained therein, such as cost center, G/L account, item account assignment, etc. In this way, a semantic model is created that is continuously enriched with all information related to the cost invoices. In short, the algorithm designs a schema for future recurring cost accounts or the goods, commodities or materials concerned.
A guide to automated procure-to-pay processes in SAP
How does the processing of the calculations with AI work?
The algorithm consists of two methods working in parallel: the static method and the dynamic method.
Static procedure
The static procedure refers to the content of an invoice, i.e. the delivered goods or services. It is not limited to certain vendors or company divisions. The static procedure evaluates, for example, all invoices for a product, regardless of the supplier or the area of the company from which the product was ordered. For the evaluation, the AI uses both the OCR information read from the invoices and the corresponding posting information of the corresponding SAP FI documents.
Dynamic procedure
In contrast to the static procedure, the dynamic procedure is vendor-specific. Here, the information of the cost accounting of the respective vendor is evaluated just-in-time, while it is processed in the d.velop document reader.
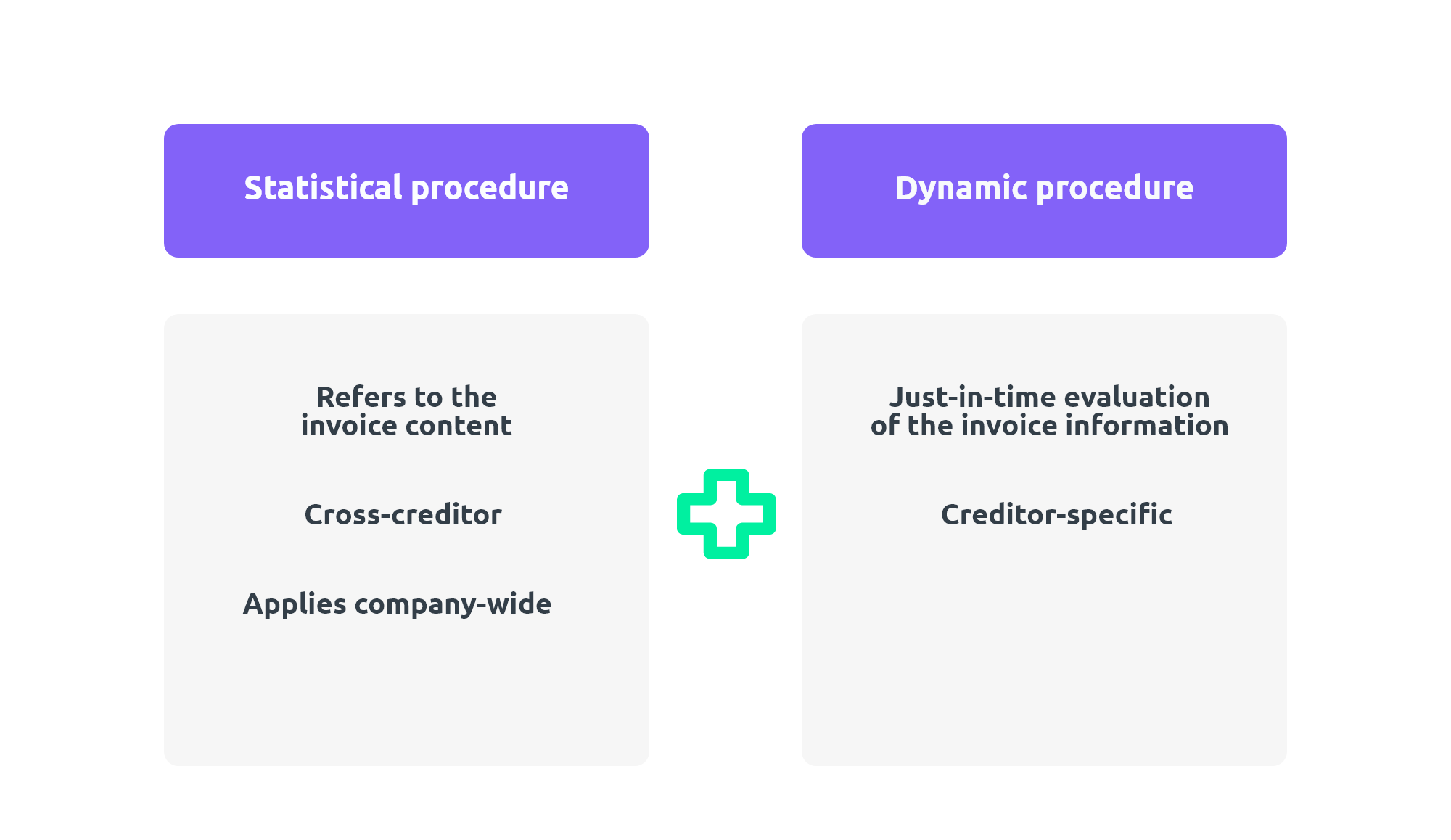
The combination of these two procedures and the information obtained in them allow proposals for the account assignment of a wide variety of recurring cost accounts.
The AI learns with every invoice processed
The AI can achieve particularly high-quality account assignment proposals if it can draw on an extensive history. It is ideal if the information from 200-300 invoices already processed and the associated posting records can be evaluated. If less or no historical data is available, the AI makes a current account assignment suggestion. This is further optimized over time and with each new cost accounting.
The user has the choice
The determined proposal for the account assignment of the cost accounting consists of the G/L account(s), as well as cost centers, orders and WBS elements. Of course, the users still have the free choice. The account assignment proposal of the AI can be accepted directly, modified or ignored. By changing or ignoring the proposal, the AI learns and provides an optimized account assignment proposal for the next cost accounting.
Conclusion: AI enables automation in the account assignment of SAP FI cost accounting.
AI enables automation in the account assignment of SAP FI cost accounting. This not only significantly reduces the effort required for this work step, but also frees up employees for other activities. Last but not least, this can increase employee satisfaction.
