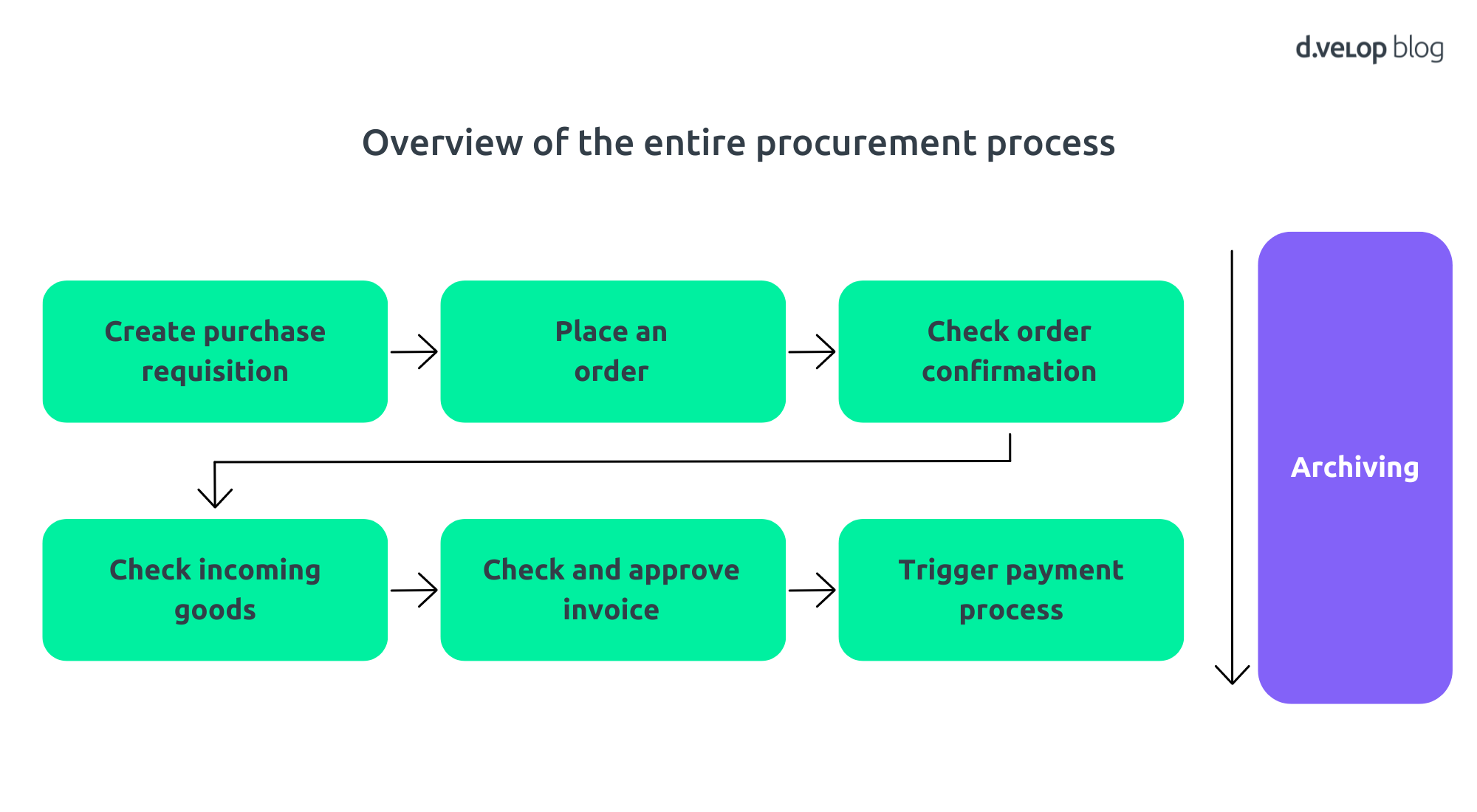
A critical process within a company is the procurement process. Securing goods, raw materials and services are crucial and decisive for economic activities and success of a company. So, let’s take a closer look at the process: What exactly does it look like? What challenges are there? And how can digital solutions help with process optimisation?
Definition Procurement Process
The procurement process includes all activities that deal with the planning and purchasing of goods and services. It ensures the control of volume and the economical supply of satisfactory quality goods. With the aim of receiving the right goods, in the right place, the right quantity and at the right time.
The 6 steps of the procurement process at a glance
1. The needs assessment
In the needs assessment step, the need for certain resources, goods or services is analysed and identified. This often happens through automated demand planning, which depends on other factors, such as production planning or inventory levels.
2. The demand requirement
For efficient and careful procurement, it is important to order the right goods from the right supplier in the right quantity to the right place. That sounds simple, but that doesn’t always correspond to reality. The requirement request is a formalised request to purchasing and ensures central communication of the requirement. This process can best evaluate which supplier the goods are ordered from, optimise use of negotiated conditions, order the right goods and thus prevent the maverick buying effect. This effect describes “wild purchasing behaviour”, with many employees ordering goods, with no attention paid to the correct choice of suppliers, price or even, possible duplication of orders.
3. Supplier management
Supplier management is a crucial aspect of the procurement process. The right suppliers are selected and delivery conditions are negotiated. Drawing up supplier contracts is also an important part of the process. Negotiation goals and corporate positioning are established for an optimal negotiation result.
4. Obtaining and comparing offers
When obtaining offers, information such as perfect order fulfilment, prices, payment terms and quality of the goods are crucial aspects. They are the basis for the offer to be made by the suppliers. These are also the crucial components for comparing offers. The ordering company weights the components of the offer according to its individual situation. For example, if the desired goods are currently in short supply, the delivery date is crucial; if the ordering company is currently not very liquid, the price or payment terms play a larger role.
5. Order
The order is placed following the final selection of the most applicable offer, this aligned with previous requirements and the corporate selection criteria. The order is usually placed by the purchasing department and later forms the basis for checking the order confirmation and for receipt of goods.
6. Invoice processing
Invoice processing completes the procurement process. The purchased goods must be paid for depending on the specified payment date. The efficient processing and sign off of invoices, is crucial to managing financial transactions and obtaining full benefit from negotiated terms in the procurement process.
Challenges in the procurement process
The procurement process brings with it some challenges for companies. An increasingly central problem is the poor ability to deliver certain raw materials due to various global influences. Companies are forced to actively manage risk in order to make needed goods available. In addition, strong price fluctuations present companies with further challenges in terms of planning. Strategic planning, coordination and monitoring are more important than ever.
Another key challenge in the process is compliance. The procurement process is subject to various compliance and legal requirements. The laws regarding ethical standards, environmental regulations, customs regulations and compliance are becoming increasingly strict. Companies are obliged to monitor compliance and, if necessary, initiate measures at an early stage.
How efficient can the procurement process be?
In addition to the challenges in the procurement process caused by external influences and specifications, the procurement process can present challenges in the area of performance. A poorly designed and non-automated process can simply be inefficient. For example, non-transparent processes can lead to a high investment of time and subsequently, result in increased process costs.
Digitalisation ensures efficiency
On the other hand, holistic digitalisation of the procurement process ensures efficiency potential. As an example:
- Operational activities, such as comparing orders and order confirmations, transmission of process-relevant documents to the people involved, can be automated and digital.
- The representation of all processes on a digital interface offers transparency for everyone involved in the process.
This saves time, resources and costs, whilst allowing the purchasing department to concentrate on strategic tasks such as securing supply chains.
Download a guide to automated procure-to-pay processes in SAP 💻
The future of the procurement process with d.velop
Digitalisation enables processes to be streamlined and those involved in the process can move away from operational activities and towards strategic tasks. As part of Purchasing 4.0, the focus is on automation that can learn and make decisions as technical support for all procurement tasks. Due to increasing challenges in the areas of delivery capabilities or price fluctuations, purchasing must increasingly focus on strategic actions. This requires relief in the operational area and can be solved with the help of the d.velop platform. Because d.velop offers a digital platform for all components of the procurement process, natively integrated into SAP. In this way, procurement processes in SAP can be mapped completely digitally and transparently for everyone involved.
Curious? Then simply book a non-binding software demo.