The digital transformation in the industry is progressing. Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT) and Digital Twins are becoming increasingly important and are opening up new potential for efficiency and sustainability. Nevertheless, almost two thirds of companies with fewer than 500 employees see themselves as laggards in this area, which indicates an urgent need for action. In this blog article, you will find out everything you need to know about Industry 4.0 — about the current technological trends, opportunities, and risks. But first, let’s clarify something fundamental:
Definition and Characteristics: What is Industry 4.0?
In simple terms, Industry 4.0 generally describes an innovation and transformation process within the manufacturing industry. The aim of the process is to merge the real world with the virtual world. Using state-of-the-art digital information and communication technology, the aim is to create intelligent networking between people, machines and industrial processes.
New Opportunities for Companies through Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 offers enormous potential for large corporations, SMEs and small businesses alike. Industry 4.0 digitalisation not only opens up new prospects for employees, but also new organisational and control options for the entire value chain. Innovative forms of economic activity and work represent the guard rails for the intelligent linking of the aforementioned human, machine and process factors.
Implementing digitalisation and networking with IT security
One of the world’s leading Industry 4.0 networks is the Industry 4.0 platform. In addition to targeted recommendations for action for companies, science and politics, the participants in the Industry 4.0 platform are developing plans for how digitalisation and networking can be implemented in the future in line with IT security standards. The platform also supports small and medium-sized companies in particular in overcoming the challenges of Industry 4.0.
The industrial revolution: 4 steps to Industry 4.0
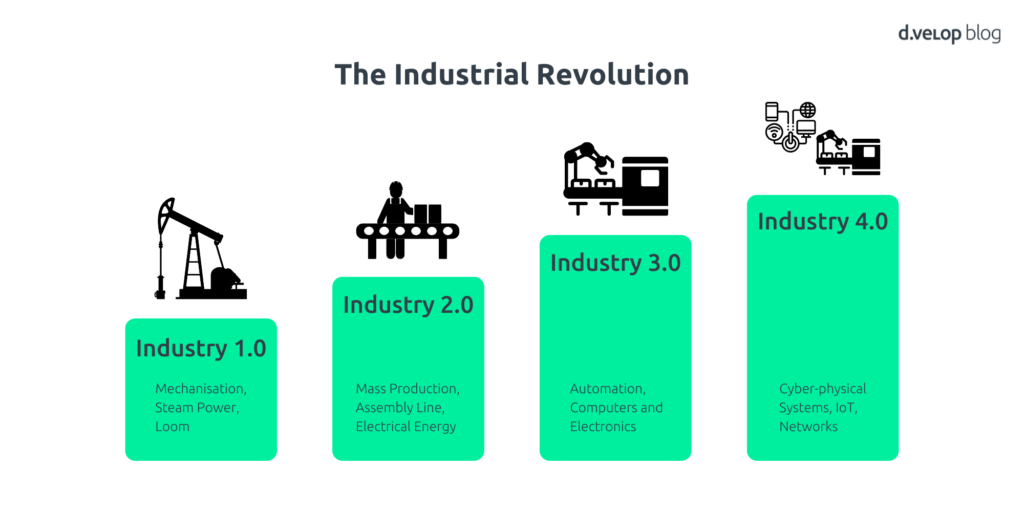
It is no coincidence that machines can now communicate with each other via the internet and carry out complex processes automatically. People have always tried to simplify their work by using tools to improve processes and make them more efficient. In industry, this has taken place in four stages. Here is an overview of the evolution of the industrial revolution up to Industry 4.0 as we know it today:
- Industry 1.0 (late 18th century) — The invention of the steam engine began the mechanisation of production, replacing manual labour with machines. This laid the foundations for modern production processes and factories.
- Industry 2.0 (early 20th century) — The introduction of the assembly line and electrification revolutionised mass production, greatly increasing efficiency and scalability. Communication and information technology also improved the control and management of production.
- Industry 3.0 (1970s) — Automation through electronics, IT and the first robots optimised production processes. Digital control systems and robotics significantly increased efficiency and precision.
- Industry 4.0 (today) — Since the end of the 20th century, the Internet has grown in importance as a central technology in industry. Since 2011, the term ‘Industry 4.0’ has stood for increasing digitalisation and networking. The Internet of Things (IoT) and intelligent technologies such as artificial intelligence have played a key role in shaping digitalisation 4.0 in industry. Networked machines, machine learning (ML) and the digital twin enable intelligent, self-optimising production. This digitalisation 4.0 offers new opportunities and risks, as it makes processes more flexible and efficient, but also poses challenges in terms of management and IT security.
Examples of the opportunities and risks of Industry 4.0
Digitalisation and Industry 4.0 offer far-reaching opportunities and challenges for companies. These show that forward-looking management is crucial for successfully shaping the transition to Industry 4.0:
Opportunities of Industry 4.0
- Increased efficiency and productivity: Production processes can be optimised and carried out faster through automation and digital networking.
- Reduced costs: Automated processes and optimised use of resources reduce operating costs in the long term.
- Active conservation of resources to invest them in other areas: Intelligent systems utilise materials and energy more efficiently, freeing up savings for innovation.
- Fully transparent processes: Real-time data enables seamless traceability and control along the entire value chain.
- Fast, flexible response to market changes: Networked systems and AI-supported analyses allow agile adaptation to change customer needs and market conditions.
- Machines can react autonomously to changing requirements: Machine learning and intelligent sensors enable production systems to adapt autonomously.
- By collecting and analysing data, new solutions can be developed and work processes optimised: Big data and AI help to recognise patterns and develop innovative business models.
- New working models for employees: Digitalisation enables working from home, more flexible working hours and location-independent collaboration.
- Support through complete information procurement and relief for older employees through load robots, for example: smart assistance systems make physically demanding tasks easier and improve knowledge transfer.
- Improving the work-life balance and increasing employee satisfaction by flexibly adapting work processes: Automation can take over monotonous tasks and offer employees more freedom for creative activities.
- New growth opportunities and competitive advantages for Germany as a business location: Technological innovations and digitalisation strengthen the global competitiveness of German companies.
- Flexible production environments: Modular and networked production lines enable rapid customisation to individual customer requirements.
Risks of Industry 4.0
- Increased demands on IT security due to large amounts of data to protect against data misuse: companies must invest in robust security solutions to prevent cyberattacks and data leaks.
- Limited social acceptance due to new working models, for example (focus on knowledge work instead of physical labour): The transformation from traditional jobs to digital professions can lead to resistance and uncertainty among the population.
- Increasing shortage of skilled labour, for example IT experts, due to changing demands on employees: Increasing digitalisation requires specialised professionals whose training and availability are currently inadequate.
Digitalisation 4.0: How companies can increase their efficiency
The Internet of Things (IoT) marks the starting signal for Industry 4.0. The intelligent networking of machines enables full automation, such as the maintenance of machines, which they now carry out independently. Human access to a machine is only required in exceptional cases. By connecting machines wirelessly to the internet, they can independently collect, analyse and link information and share it with other machines.
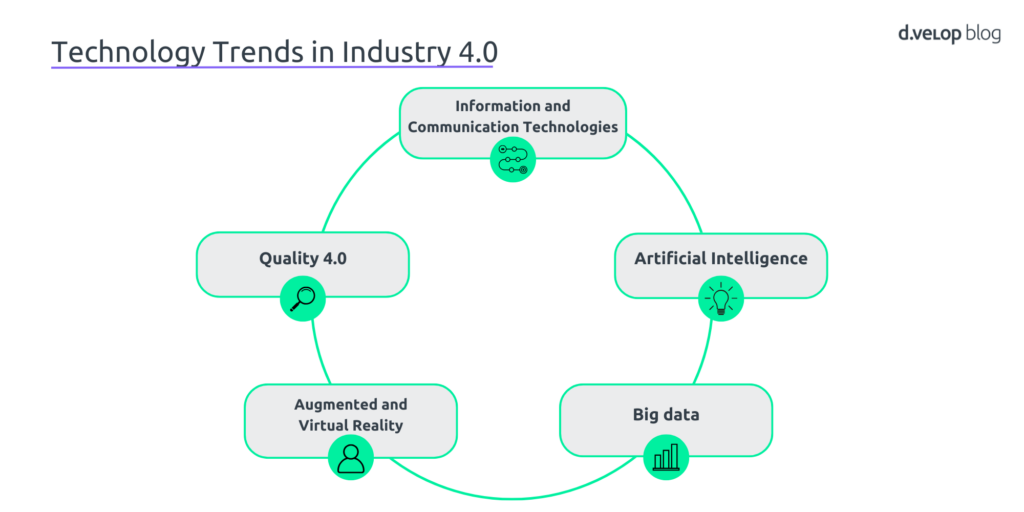
Important technologies and concepts
Whether new artificial intelligence technologies, augmented reality and virtual reality or big data – software that supports Industry 4.0 processes offers industrial companies enormous advantages in the manufacture of products and services. Examples of important technologies in relation to Industry 4.0 include
1. Information and communication technologies as a basis
They play a central role in Industry 4.0. Efficient production is simply not possible without high-performance communication technology. This applies to wireless data transmission, for example for networking machines in production, as well as for the use of VR.
2. Artificial intelligence simplifies work steps
Efficient production is important in every industrial company. This is where artificial intelligence comes in, as modern Industry 4.0 technologies teach machines to develop their own functions. This enables them to perform better when carrying out work steps. AI thus enables machine learning and the associated continuous product improvements, as well as the emergence of new business models.
3. More targeted action decisions with big data
The amount of data in companies continues to grow. Digitalisation and Industry 4.0 are responsible for this. This is exactly what big data describes. By analysing these large amounts of data, companies can gain a lot of useful information. Intelligent, self-learning algorithms can be used to create links between individual pieces of data. This enables industrial companies to make more targeted decisions based on better predicted data and utilise knowledge in a more targeted manner.
4. Discover the Diverse Possibilities of AR and VR
Computer-based models like VR offer customers an entirely new shopping experience, whether it’s a virtual tour of the production process or experiencing a new product. The modern technologies of Industry 4.0 can also simplify and make work steps more efficient. Information about inventory can be easily accessed via smartphone or tablet. For example, the process of a spare parts request during machine maintenance can be accelerated through the use of AR.
5. Quality 4.0
Discovering untapped potential in production? Through quality management in Industry 4.0, companies optimise — the quality of their entire value chain using the latest technologies. AI and Big Data enable extensive quality analyses. With the most advanced Industry 4.0 software, companies can quickly respond to potential errors or identify bottlenecks.
Practical examples: How companies are utilising Industry 4.0
The following examples show how companies in various sectors are utilising Industry 4.0. Networking, automation and real-time data analysis play a central role here:
Production 4.0 — The future of manufacturing
Industry 4.0 is revolutionising manufacturing through the use of state-of-the-art technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart automation. Companies in the manufacturing industry benefit from customised products at the price of mass-produced goods — and with the highest quality. Digital twins and predictive maintenance ensure shorter production cycles and autonomous machine repairs. Mechanical engineering, logistics and services are already networked today and communicate with each other autonomously in order to organise processes more efficiently. Dynamic production enables rapid adaptation to market changes and increases competitiveness.
Industry 4.0 in the automotive industry — trend towards individualisation
Data is the new gold — especially in the automotive industry, where vehicle and customer data are key success factors. Industry 4.0 enables intelligent networking of this data so that manufacturers can focus on personalised vehicles and customised services. Companies that previously focused purely on pricing are increasingly orienting themselves towards individualised mass production. Human-machine collaboration is central to this change: while service robots take on heavy or dangerous tasks, humans retain control and supervision thanks to their cognitive abilities. 20% of automotive companies already use self-controlling systems in production — a trend that is continuing to grow.
Mechanical engineering 4.0 — automation through cobots
Industry 4.0 has long been an integral part of the corporate strategy of large mechanical engineering companies. Digital technologies such as autonomous transport systems, networked logistics solutions and predictive maintenance increase efficiency and reduce costs. Collaborative robots (cobots), which support employees in physically demanding tasks, are a particular focus. Smart technologies such as data glasses, 3D printing and software bots are also being used to automate and optimise work processes. This digital transformation enables more flexible production, increases safety in the workplace and improves the utilisation of resources.
Industry 4.0 in the Chemical Industry – Digital Progress Without Limits
The chemical industry is one of the largest users of digitalisation technologies, as it faces strong international competitive pressure. Industry 4.0 opens up almost unlimited possibilities: Smart sensors monitor product quality in real-time, while AI-supported systems use raw materials more efficiently. Especially in the agricultural sector, farmers benefit from digital solutions such as precise fertilizer application or automated soil analysis. Through close collaboration between chemical companies and agriculture, sustainable, resource-saving solutions are created that combine efficiency and environmental friendliness. In the next section, we will examine how Agriculture 4.0 is transforming the agricultural sector.
Agriculture 4.0 – Smart Technologies for a Sustainable Future
Efficiency improvement, sustainability, and digitalisation shape the future of agriculture. Technologies such as Big Data, AI, agricultural apps, and autonomous machines enable farmers to manage their operations more precisely and resource-efficiently. Self-driving harvesters, drones for field monitoring, and intelligent irrigation systems increase productivity and relieve physically working professionals. However, a major obstacle remains the often inadequate network coverage in rural areas. Nevertheless, Agriculture 4.0 opens up enormous opportunities for a sustainable, technology-based agricultural economy that meets the increasing demands of food production.
Logistics 4.0 – Efficiency Through Smart Networking
A connected, digitally controlled logistics system is the backbone of Industry 4.0. Logistics 4.0 uses real-time data for shorter delivery times, optimised demand planning, and greater transparency along the supply chain. Technologies such as GPS, sensors, barcodes, and AI enable seamless integration of all transport and storage processes. Self-driving transport vehicles and intelligent goods that independently book transport slots or manage inventory are revolutionizing the entire value chain. Thus, Logistics 4.0 becomes a crucial competitive factor in an increasingly digitalized economy.
Get an insight into the software now! 💻
Is Industry 4.0 Still Relevant?
Industry 4.0 remains relevant as many companies are still in the midst of digital transformation, implementing technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation. However, Industry 5.0 is gaining importance, especially since the European Commission published a white paper in 2021 that places a greater focus on humans.
Industry 5.0: Sustainability, Resilience, Human-Machine Interaction
While Industry 4.0 focuses on connectivity, efficiency, and automation, Industry 5.0 complements these concepts with sustainability, resilience, and stronger human-machine interaction. Industry 4.0 concentrates on optimizing production processes, whereas Industry 5.0 aims to place greater emphasis on social and ecological aspects. Both concepts exist in parallel, with Industry 5.0 representing an evolution rather than a replacement of Industry 4.0.
Voices: “I’m Already at Industry 9.0”
In online forums like Reddit, there is much discussion about various aspects of “Industry 5.0.” We present some positions without comment to document the diversity of viewpoints:
- “Meaningless buzzword 5.0.” — One user considers Industry 5.0 to be just a buzzword.
- “AI for training vision systems will be a big win.” — Others see useful applications for AI, especially in image processing.
- “With AI and Industry 5.0, it’s not about replacing maintenance teams, but making them better.” — One user clarifies that AI aims to improve processes rather than replace workers.
- “I’m already at Industry 9.0.” — A humorous comment criticizing the often exaggerated advancement of such concepts.
- “The integration of humans and machines makes the industry more human again.” — One user believes that Industry 5.0 emphasizes human-technology interaction.
- “It’s not just about efficiency, but also about sustainable development.” — This user focuses on the environmental and socially responsible innovations of Industry 5.0.
- “The challenge lies in implementation in large companies.” — Another user warns of practical difficulties that larger firms might face when introducing Industry 5.0.
Industry 4.0 is no longer just a vision of the future. The fourth industrial revolution has already begun. Take the opportunity to make processes more efficient.
